MIG Welding vs. TIG Welding : Which Welding Process Is the Best for Your Application?
Welding is a process that involves joining two pieces of metal by melting them and allowing them to cool, forming a solid joint. There are many welding techniques available, with two of the most popular being MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding. While both methods involve heat generated by an electrical current melting the base and bonding materials, there are important differences between the two that make them better suited for different applications.
TIG Welding: Benefits and Applications
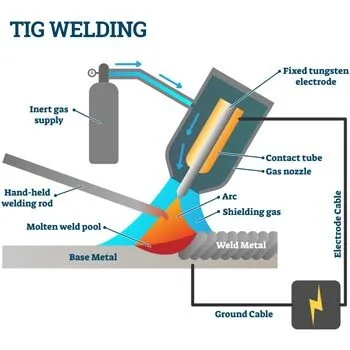
tig welding process illustration
TIG welding is highly versatile, making it ideal for joining small and thin materials. It uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to heat the metal and can be used with or without a filler. While it is slower than MIG welding, it offers greater control during the welding process and produces precise and aesthetically pleasing welds. Welders require specialized training to achieve the required precision and accuracy for TIG welding. This method is commonly used in industries where appearance and precision are important, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries.
MIG welding, on the other hand, is generally used for large and thick materials. It uses a consumable wire that acts as both the electrode and the filler material. This method is faster than TIG welding and produces welds that require little to no cleaning or finishing. It is also easier to learn than TIG welding, making it a popular choice for both industrial and DIY applications. However, its welds are not as precise, strong, or clean as those formed by TIG welding.
Find out more:TIG welders – click here
MIG Welding: Benefits and Applications
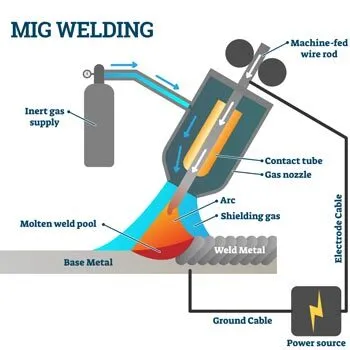
mig welding process illustration
Metal inert gas (MIG) welding is typically utilized for welding large and thick materials, using a consumable wire that functions as both the electrode and filler material. This welding process is much faster than TIG welding, which leads to shorter lead times and lower production costs. Moreover, MIG welding is easier to learn and results in welds that require minimal cleaning and finishing. Nonetheless, the welds created through MIG welding are not as accurate, durable, or polished as those produced by TIG welding.
Typical Materials Used in MIG and TIG Welding Operations
Both MIG and TIG welding can be used on a wide range of metals, including aluminum, carbon steel, and stainless steel. However, MIG welding is more suitable for thicker materials, while TIG welding is better suited for thinner materials. Ultimately, the choice between MIG and TIG welding depends on the specific needs of the application, such as the type and thickness of the metal being welded, as well as the desired finish. Welders need to consider the benefits and limitations of both methods before choosing the one that best fits their requirements.
See our full range of MIG welders – click here


