What Is a Multi-Process Welder And What Can It Be Used For
A multi-process welder is a type of welding machine that is capable of performing various welding techniques such as MIG, TIG, Stick, and Flux-Cored welding. It is a versatile machine that can handle a variety of welding projects and materials.
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding is a popular welding technique that uses a wire electrode and a shielding gas to create an electric arc that melts the wire and the base metal together. This technique is commonly used in the automotive, construction, and manufacturing industries.
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding uses a tungsten electrode and a shielding gas to create an electric arc that melts the base metal. TIG welding is known for its precise and high-quality welds and is commonly used in aerospace, motorsports, and artistic welding.
Stick welding (also known as Shielded Metal Arc Welding) uses an electrode coated in flux to create an electric arc that melts the base metal and the electrode. This technique is commonly used in construction, maintenance, and repair welding.
Flux-Cored welding uses a wire electrode that is filled with flux to create an electric arc that melts the wire and the base metal. This technique is commonly used in heavy fabrication, shipbuilding, and pipeline welding.
A multi-process welder can switch between these different welding techniques quickly and easily, allowing the user to perform various types of welding without having to switch machines. This can save time, money, and space in a welding shop or job site.
Overall, a multi-process welder is a versatile and efficient machine that can handle a variety of welding projects and techniques, making it a valuable tool for both professional welders and hobbyists.
How Does a Multi-Process Welder Work?
A multi-process welder works by using a combination of different welding techniques and technologies to create a versatile welding machine. Here’s a general overview of how it works:
- Power source: A multi-process welder has a power source that provides the necessary current and voltage for the different welding processes.
- Control panel: The control panel on a multi-process welder allows the user to select the desired welding process, adjust the settings for that process, and monitor the machine’s performance.
- Wire feeder: The wire feeder is a component of the welder that feeds the welding wire to the welding torch at a precise rate. The wire feeder is a critical part of MIG and Flux-Cored welding.
- Torch: The welding torch is used to create the electric arc that melts the metal and performs the welding. The torch may use a different type of electrode depending on the welding process being used.
- Gas source: For MIG and TIG welding, a gas source is used to provide a protective shield around the welding area to prevent contamination.
- Multi-process capabilities: A multi-process welder can switch between different welding processes by adjusting the settings on the control panel. The machine can be set up for MIG, TIG, Stick, or Flux-Cored welding.
When the user selects the desired welding process and adjusts the settings, the power source provides the necessary current and voltage, the wire feeder feeds the welding wire to the torch, and the torch creates the electric arc to melt the metal and perform the welding. The multi-process welder can perform different welding techniques without having to switch machines, making it a versatile and efficient tool for welding projects.
A multi-process welder can perform more than one of the following welding methods:
- MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding
- TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding
- Stick welding (also known as Shielded Metal Arc Welding)
- Flux-Cored welding
A multi-process welder is designed to handle a variety of welding projects and materials by allowing the user to switch between different welding techniques quickly and easily. This can save time, money, and space in a welding shop or job site.
For example, a welder may start with MIG welding for a particular project, but then switch to TIG welding for a more delicate area that requires a higher level of precision. Alternatively, a welder may switch to Stick welding for a project that requires higher penetration, or to Flux-Cored welding for welding thicker materials.
The ability to switch between these different welding techniques without having to switch machines makes a multi-process welder a versatile and efficient tool for welding projects.
Are Multi-Process Welders Worth It?
Multi-Process welders, also known as multi-process welders, can be a great investment for welders who need to perform a variety of welding techniques. Here are some factors to consider when determining if a multi-use welder is worth it:
- Versatility: Multi-Process welders can perform more than one welding technique, which makes them versatile tools for welding projects. This versatility can save time and money by allowing welders to perform multiple tasks without having to switch machines.
- Cost: Multi-Process welders can be more expensive than single-process welders, so it’s essential to consider the cost and budget when determining if it’s worth it. However, the ability to perform multiple welding techniques can offset the cost by eliminating the need for multiple machines.
- Skill level: Multi-Process welders can be more complex to use than single-process welders, which means that they may not be suitable for beginner welders. However, if you have experience with multiple welding techniques, a multi-use welder can be an excellent investment for your welding career.
- Portability: Multi-Process welders can be larger and heavier than single-process welders, so portability may be an issue. However, many multi-use welders are designed with portability in mind, so it’s essential to consider this when selecting a model.
In summary, Multi-Process welders can be worth it if you need to perform multiple welding techniques and have the budget and experience to use them effectively. The versatility and efficiency of multi-use welders can make them valuable tools for welding projects.
Perfect Power welders offer excellent value
Unless you’re a full-time professional welder, you probably don’t need a welding machine dedicated to each type of welding. Buying these individual machines if you’re a beginner or a hobbyist is not cost-effective since each machine can run between $500 and $750.
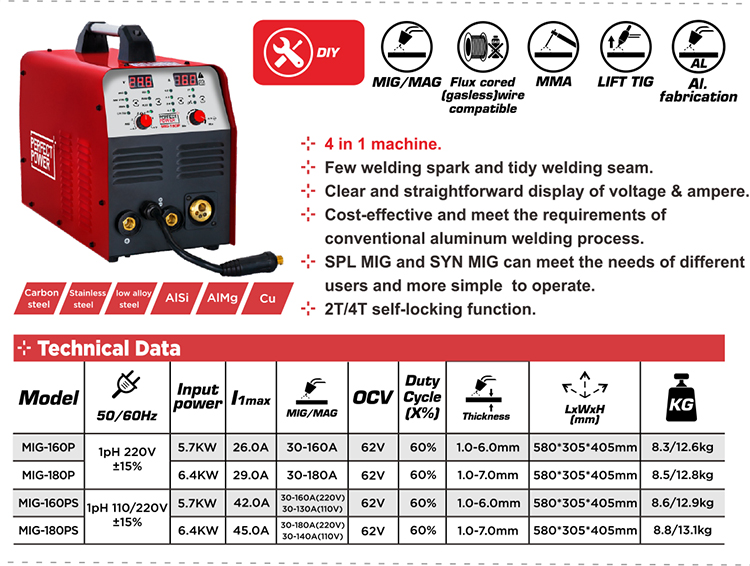
MIG-180P MIG Welding
For comparison’s sake, a MIG-180P 1800-amp 5-in-1 welder—TIG, MIG, double pulsed mig, stick, and flux cored wire welding —costs around $280 from Perfect Power Welders. Why pay for specialized features when you can have a high-quality Perfect Power machine in your workshop or at work for a fraction of the cost?
Who Is Using The Multi-Process Welder?
Here are some examples of who would use a multi-purpose welder:
- Professional welders: Professional welders who work on a variety of welding projects can benefit from a multi-purpose welder. They can perform multiple welding techniques with one machine, saving time, money, and space in their workshop or job site.
- Hobbyists and DIY enthusiasts: Hobbyists and DIY enthusiasts who enjoy welding can benefit from a multi-purpose welder. They can use one machine to perform multiple welding techniques, which can be convenient for those who have limited space and resources.
- Welding students: Welding students can benefit from a multi-purpose welder as they learn and practice different welding techniques. It can be a valuable tool for their training and education.
- Maintenance and repair technicians: Maintenance and repair technicians who work in various industries such as automotive, construction, or manufacturing, can benefit from a multi-purpose welder. They can perform multiple welding techniques with one machine, making it easier to repair or maintain equipment and machinery.
- Fabricators: Fabricators who work with a variety of materials and thicknesses can benefit from a multi-purpose welder. They can perform multiple welding techniques with one machine, saving time and increasing efficiency in their work.
In summary, a multi-purpose welder can be used by a wide range of individuals and industries, including professional welders, hobbyists, and DIY enthusiasts, welding students, maintenance and repair technicians, and fabricators. Its versatility and convenience make it a valuable tool for welding projects.


